Introduction
A Content Delivery Network or CDN for short is a network of servers distributed across the world that work together in order to deliver online content quickly. It is intended to reduce latency in web page loading by shortening the physical distance between the server and the end-user.
CDN’s help reduce lag and delays for users in different countries and are frequently deployed for high-traffic websites such as eCommerce, video websites like YouTube and forums/discussion boards with lots of images.
How CDN’s work and why they are useful
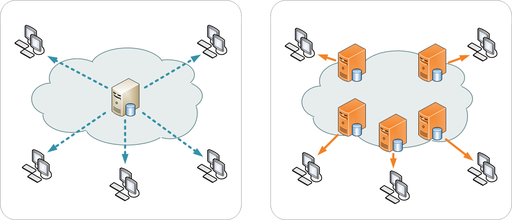
A website is limited to a country where it is hosted and will generally have fixed resources allocated such as network bandwidth, storage and RAM.
This system works fine for traffic within that country however if a website needs to scale and handle traffic overseas a hosting server on it’s own may not be able to keep up and won’t be as efficient.
A CDN however acts as a middle man by storing assets of a website that are generally static such as images, JavaScript and HTML content of the page and will serve that to a user from a data-center closest to their location thus saving resources of the main hosting server.
For example if example.com has lots of content that gets visitors from Germany and example.com is hosted in the United States German visitors will get served content from a server in Frankfurt or Hamburg which will be much faster for them without putting extra strain on the U.S infrastructure.
P2P CDN’s (peer-to-peer)
Clients in peer-to-peer (P2P) content-delivery networks both provide and use resources. This means that, in contrast to client–server systems, content-centric networks can actually perform better as more users access the content (especially with protocols such as Bittorrent that require users to share content).
This property is one of the primary benefits of using P2P networks because it reduces the setup and operating costs for the original content distributor.
Security functionality & DDoS protection

Some CDN systems also offer advanced security functionality to protect against sophisticated attacks along with DDoS attempts.
A DDoS (Distributed Denial Of Service) attack is a type of attack where large volumes of illegitimate traffic is sent to a website in order to overwhelm the server and crash the target website.
Having a WAF (Web Application Firewall) in place alongside a CDN can help mitigate a DDoS attack by dispersing the traffic across high capacity data-centers and filtering out suspicious traffic before it even hits your main server.
AGR Technology can provide WAF solutions with a CDN for added performance and security.
FAQs related to CDN technology
How much does it cost to use a CDN?
The cost of a CDN might vary greatly depending on the provider, the volume of traffic, and the functionality you demand. Some CDNs provide free, limited-feature plans, while others charge based on bandwidth usage or other criteria.
Can content delivery networks (CDNs) help with website security?
Yes, CDNs frequently incorporate DDoS protection, SSL/TLS encryption, and Web Application Firewall (WAF) capabilities. These features can improve your website’s security and defend it from numerous internet dangers.
Can CDNs be used to stream media such as videos?
Yes, CDNs are often utilised for media streaming. They can efficiently transport video and audio information by utilising adaptive bitrate streaming and other technologies to provide viewers with a seamless viewing experience.
Can content delivery networks (CDNs) help with website security?
Yes, CDNs frequently incorporate DDoS protection, SSL/TLS encryption, and Web Application Firewall (WAF) capabilities. These features can improve your website’s security and defend it from numerous internet dangers.
What role does a CDN play in handling dynamic material and personalised experiences?
CDNs are typically intended for static content caching, however some modern CDNs offer dynamic content by utilising techniques such as edge computing, API acceleration, and serverless computing to efficiently deliver personalised experiences.
What are the most prevalent issues that arise when using CDNs?
Cache consistency, content purging, HTTPS configuration, cost management, and ensuring that the CDN successfully serves material from the nearest edge servers are all potential challenges.
Conclusion
If you found this page to be useful be sure to check out our other glossary entries for other technical terms and share the page with your friends and family.
AGR Technology is a Shepparton based business providing clients with a range of solutions such as Website Design & Hosting, SEO, Software Development and more.
To find out more check out our services, software tools and blog for more.
Related terms:
IaaS (Infrastructure as a service)
LMS (Learning Management System)
Image credit/References:
Kanoha, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Content_delivery_network
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)